Our guide to Payroll in India
With an estimated GDP of $3.39 trillion. India’s growth as a major international economy has attracted investment interest from sources around the globe.
Access expert analysis on India’s payroll, income tax, social security, labour law, and visas. Stay compliant in one of the world’s largest economies.
1. Introduction to Our guide to Payroll in India
2. Setting Up a Business
3. Employment Practices
4. Taxation & Social Security
5. Payroll Operations
6. Hiring & Termination
7. Compensation & Benefits
8. Visas & Work Permits
9. Location-Specific Considerations
1. Introduction to Our guide to Payroll in India
Doing Business in India
India is one of the world’s fastest-growing economies and a significant hub for global investment. The country offers large-scale opportunities across industries including technology, pharmaceuticals, infrastructure, and manufacturing. With improving regulatory environments and digital governance reforms, foreign direct investment (FDI) continues to play a major role in India’s economic expansion.
Basic Facts about India
| Full Name: | Republic of India |
| Population: | 1.417 billion (World Bank, 2022) |
| Capital: | Delhi |
| Major Language(s): | Hindi, English |
| Major Religion(s): | Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism |
| Monetary Unit: | Indian Rupee (INR) |
| Main Exports: | Software, petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, textiles, precious stones, automobiles |
| GNI Per Capita: | USD $2,410 (2022) |
| Internet Domain: | .in |
| International Dialing Code: | +91 |
Common Phrases (India – Hindi)
Hello: नमस्ते (Namaste)
Good Morning: शुभ प्रभात (Shubh prabhaat)
Good Evening: शुभ संध्या (Shubh sandhyaa)
Do you speak English?: क्या आप अंग्रेज़ी बोलते हैं? (Kya aap angrezi bolte hain?)
Goodbye: अलविदा (Alvida) / फिर मिलेंगे (Phir milenge – "See you again")
Thank you: धन्यवाद (Dhanyavaad)
See you later: फिर मिलते हैं (Phir milte hain)
2. Setting Up a Business
Registrations and Establishing an Entity
- Obtain Director Identification Number (DIN)
- Obtain digital signature
- Reserve company name with Registrar of Companies (ROC)
- File incorporation documents online
- Obtain PAN and TAN from tax authorities
- Register under Shops & Establishments Act
- Register for GST, PF (EPFO), and ESI
- LWF and Professional Tax registration (location dependent)
Banking Employee payments can be made from abroad, but statutory payments (e.g., PF, ESI, tax) must be made from an in-country bank. Transfers take 2–3 days. Banking hours are Mon–Fri 09:00–16:00, and Sat (1st & 3rd) 09:00–13:00.
3. Employment Practices
Working Week
Typically Monday–Saturday, 09:30–18:00. Actual hours may vary by industry.
Holiday Accrual Minimum entitlement varies by state; usually 12–18 days/year. Leave encashment for unused leave is paid at standard rates.
Maternity Leave Up to 26 weeks for first two children; 12 weeks for third child. 6 weeks for miscarriage. Crèche facility required for 50+ employees.
Paternity Leave Not statutory; usually 7–10 days per company policy.
Sick Leave Leave entitlements vary by location; typically 5–12 days/year.
National Service Not applicable in India.
4. Taxation & Social Security
Tax Year
April 1 – March 31
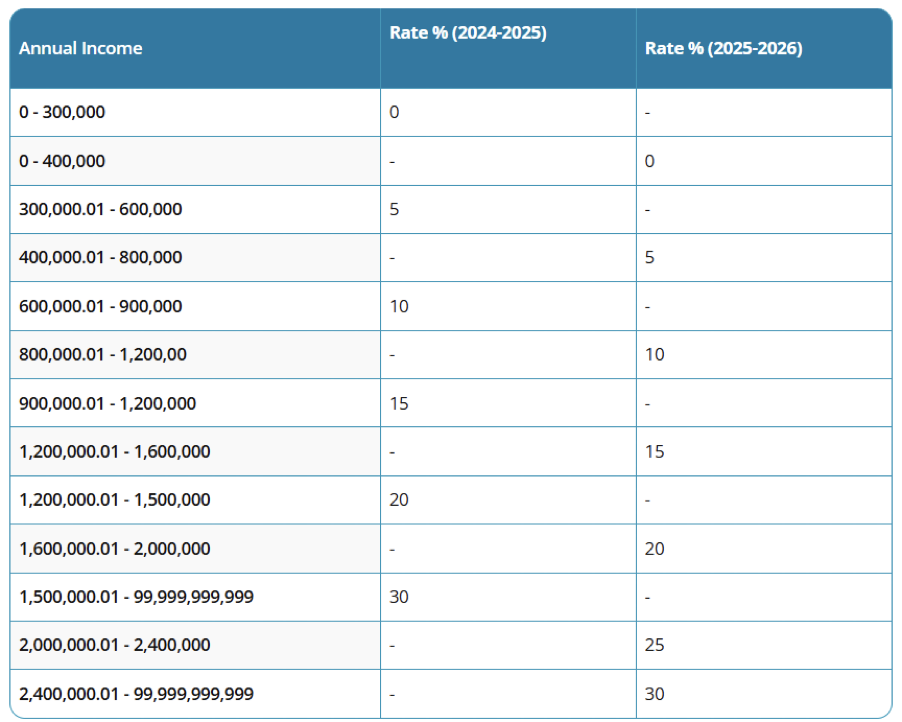
Income Tax (New Regime – from 1 April 2025)
- Up to INR 3,00,000: Nil
- INR 3,00,001 – 6,00,000: 5%
- INR 6,00,001 – 9,00,000: 10%
- INR 9,00,001 – 12,00,000: 15%
- INR 12,00,001 – 15,00,000: 20%
- Above INR 15,00,000: 30%
- Rebate u/s 87A: up to INR 60,000 for income up to INR 7,00,000
 Social Security Contributions
Social Security Contributions
- Provident Fund: 12% employee, 12% employer (8.33% to pension fund, 3.67% to PF)
- ESI: Employee 0.75%, Employer 3.25%
- Professional Tax and Labour Welfare Fund: location dependent
- EPFO reporting deadline: 15th monthly
- Interest for delay: 12% per annum; damages up to 25% depending on duration

5. Payroll Operations
Payroll
- Salary due by 7th of the following month
- 8-year payroll record retention
- Online English payslips are permitted
Reports
- Monthly: TDS (by 7th), PF/ESI (by 15th)
- Quarterly TDS Returns: Form 27A (Jul, Oct, Jan, May)
- Annual TDS Summary: Form 16 (due 15 June)
6. Hiring & Termination
New Employees
- PAN required for tax compliance (takes ~1 month to obtain)
- Registration with PF/ESI within 15 days of second month
- Passport and salary details required for expatriates
Leavers
- Final payment (F&F) due within 30 days
- Gratuity payable after 5 years of service
- Inform PF/ESI authorities of departure
Expenses
- Business expenses must be reimbursed outside of salary
- Valid invoices and receipts required for tax-free treatment
7. Compensation & Benefits
Employee Benefits
- Statutory: PF, ESI, gratuity, bonus, maternity
- Optional: medical insurance, allowances, crèche facility
Expenses
- Business expenses must be reimbursed outside of salary
- Valid invoices and receipts required for tax-free treatment
8. Visas & Work Permits
Employment Visa (EV)
- Required for employment or voluntary work with NGOs
- Valid from date of issue; renewable for up to 5 years
Required Documents:
- Passport valid for 180+ days, visa fee
- Photos, signed application and undertaking
- Employment contract specifying income tax clause
- Employer’s registration documents and applicant's educational records
9. Location-Specific Considerations
- Indian numbering system uses Lakh (1,00,000) and Crore (1,00,00,000)
- Leave, tax slabs, and welfare contributions vary by state
- PAN, TAN, GST, ESI, PF registration is mandatory for compliance
Further Information For more information, or assistance with India tax enquiries please contact: gi@activpayroll.com
About This Payroll and Tax Overview Please note that this document gives general guidance only and should not be regarded as an authoritative or complete statement of the law, regulations or tax position in any country. You should always seek specific advice for each specific situation. This document should not be relied upon as professional advice and activpayroll accepts no liability for reliance on its contents.
Talk to a specialist today and find out how we support the growth of over 500 businesses with a range of activpayroll solutions designed to help your global payroll and people operations succeed.